DISCUSSION
The beneficial effect of selenium is due to its selenocysteine amino acid, which is present in the active site of selenoproteins. For this reason these proteins exert different functions as reduction of reactive oxygen species, control of the redox status of the cell or thyroid hormone maturation. Nonetheless, the majority of selenoproteins whose function is known are oxidation-reduction enzymes [24].
GPX family have been widely studied and characterized. In a similar way have been iodothyronine deiodinases (DI) and thioredoxin reductases (TR) families. The biological functions of other selenoproteins such as SelH, SelI, SelM, SelN, SelS, SelT and SelW have been partially characterized while others (as SelK and SelO) have been hardly studied and their functions remain unknown [28].
More than half of the selenoprotein families were shared by unicellular eukaryotes and mammals, consistent with their ancient origin. Many selenoproteins originated at the base of the eukaryotic domain. Their selenoproteom evolution is highly influenced by the environment. Further analyses identified massive, independent selenoprotein losses in land plants, fungi, nematodes, insects and some protists [7].
Whereas aquatic organisms apparently retained and sometimes expanded their selenoproteomes (generally they have large selenoproteomes), the selenoproteomes of some terrestrial organisms were reduced or completely lost, through loss of selenoprotein genes and replacement of Sec with cysteine [7].
In particular, in the mammal linage the content of selenoproteins have decreased considerably [23].
According to the data, only 21 of the whole selenoproteins are found in all vertebrates [16]. The remainder are only found in certain lineages. In mammalian selenoproteomes consist of 24-25 selenoproteins, whereas lower eukaryotes and prokaryotes mostly have very few of these proteins (for example, only 4 selenoproteins have been found in Plasmodium and 3 in Escherichia coli) [23].
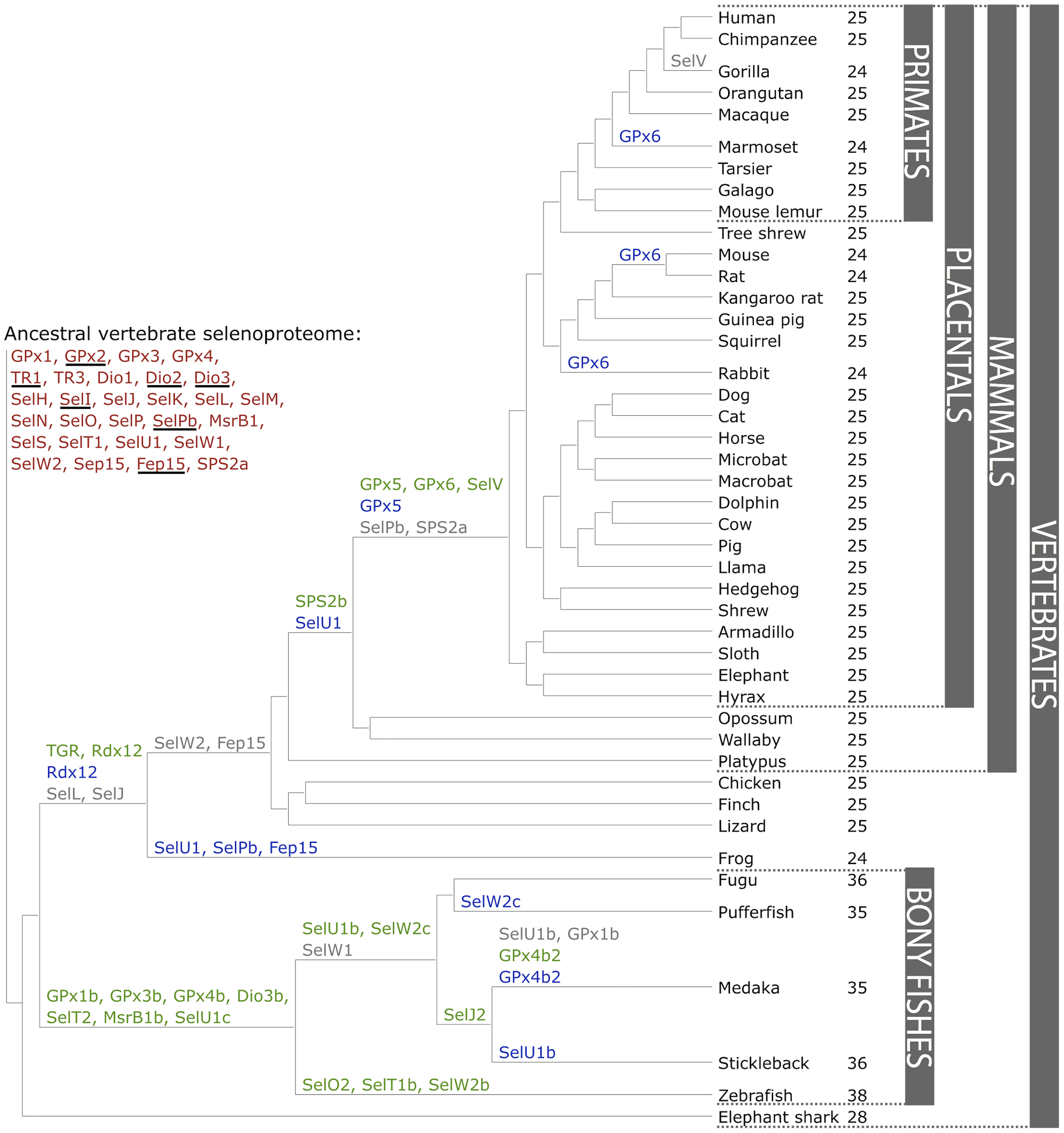
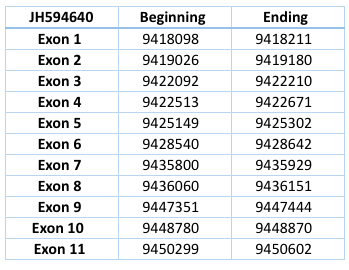
Figure 1. The ancestral vertebrate selenoproteome is indicated in red, and its changes across the investigated vertebrates are depicted along their phylogenetic tree. The ancestral selenoproteins found uniquely in vertebrates are underlined. The creation of a new selenoprotein (here always by duplication of an existing one) is indicated by its name in green. Loss is indicated in grey. Replacement of Sec with Cys is indicated in blue (apart from SelW2c in pufferfish, which is with arginine). Events of conversion of Cys to Sec were not found. On the right, the number of selenoproteins predicted in each species is shown. We observed 12 conversions to Cys along vertebrates, 8 of which happened after the split of mammals. [16].
Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) Family
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity, which catalyses the reduction of H2O2 or organic hydroperoxides to water or corresponding alcohols using reduced glutathione. The peroxidase activity of some glutathione peroxidase isozymes is selenium-dependent and presents a selenocysteine. This family appears to have redox functions, protecting cells from oxidative damage [26].
Glutathione peroxidases are the largest selenoprotein family in vertebrates. In mammals there are eight GPx proteins described. In the case of Loxodonta africana GPx1-4 and GPx6 contain a Sec residue highly conserved, and the rest contain an homologous cysteine.
It appeared that Cys-containing GPx7 and GPx8 evolved from a GPx4-like selenoprotein ancestor, but this happened prior to separation of mammals and fishes. GPx5 and GPx6 are the most recently evolved GPxs, which appeared to be the result of a tandem duplication of GPx3 at the root of placental mammals. Interestingly, no Sec-containing GPx5 form could be identified. As phylogeny indicates that this protein evolved from a duplication of selenoprotein GPx3, the Sec to Cys displacement must have happened very early in the evolution of GPx5 [16].
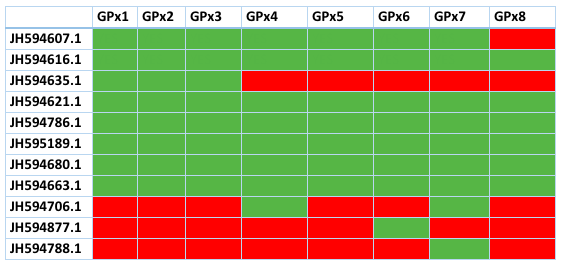
Many of the contigs of GPx are shared with most members of this family. This table shows the contigs and which proteins of Loxodonta africana have aligned with them. Green means presence, red means absence. As we can see, many of the contigs are shared by most GPx and also, the ones that are unique for one GPx had a very high E value. This latter finding suggests that the proteins are not clearly defined and more research should be made. Here we refused to explain the ones with an E value too high and the contigs than did not contain a selenocysteine or an homologous cysteine so we can't consider them selenoproteins.
Location of the GPx's
The tissue and subcellular localization of different Gpxs been determined from the human protein atlas and supported with several papers. GPx1 is located in the cytoplasm and is high expressed in cells of tubules of the kidney, in seminiferous ducts of testis, in the glandular cells of endometrium and in the follicle cells of the ovary, in the parathyroid gland and finally in the lungs. GPx2 is mainly localized in the nucleus but excluded from the nucleol and into the cytoplasm. It is specifically expressed in the gastrointestinal system protecting, especially the colon, against the ingested lipid hydroperoxides. It is also found in the urothelial cells. GPx3 is secreted to the plasma being expressed in cells of tubules of the kidney and in the macrophages of the lung. It is involved in detoxification of hydrogen peroxide. GPx4 is present in the cytosol and mitochondria in different cell types. Can act on many substrates and is particularly important in the maturation of sperm. GPx5 is specifically localized in the epididymis. GPx6 is found in the olfactory epithelium and embryonic tissues. GPx7 corresponds to the phospholipid hiperoxid glutathione peroxidase and it is located to the nucleoli. Concretely, it is highly expressed in the hepatocytes, in testis (Leyding cells), cerebellum (Purkinge cells) and adrenal gland. Finally, GPx8 is found in the cytoplasm and actin filaments being highly expressed in the stomach and in smooth muscle [3] [25].
JH594607.1
Its sequence contain 277 nucleotides (28256885-28257162) and is composed of two exons and one intron in reverse chain. It includes two fragments with an identity of 95%.
Seblastian predicted three different SECIS elements but we chose the one that was located closer to our protein. For the contig JH594607, the program SeBlastian found a SECIS item in 3' end of the chain in which is the gene situated (28256398-28256473). This SECIS with a grade A is located in a distance of 62 nucleotides from the last exon and 796 nucleotides from the selenocystein, so we can confirm that this is a selenoprotein.
It should be noted that this contig can also be found in GPx2, GPx3, GPx4, GPx5, GPx6 and GPx7. This means that we need a phylogenetic tree to confirm to which GPx it corresponds. We made a T-Coffee alignment with this contig and all the GPx of Loxodonta africana and we can see a great similarity amongst GPx1 and GPx2. There is a selenoprotein in the first exon of the gene of Trichechus manatus latirostris, which is aligned with the Sec of Loxodonta africana of the proteins GPx1, GPx2, GPx3, GPx4 and GPx6. With the rest of GPx is aligned with a cysteine.

JH594616.1
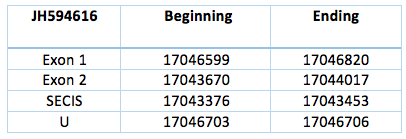
This contig is codified by two exons separated by an intron, located in the reverse chain of scaffold JH594616.1. The sequence has a length of 3150 nucleotides (17043670-17046820). The SECIS element is predicted with a grade A and is located 217 nucleotides from the second exon and 3250 nucleotides from the selenocysteine.
The Sec of Trichechus manatus latirostris is aligned with the Sec of Loxodonta africana GPx1, GPx2, GPx3, GPx4 and GPx6 and with the homologous cysteine of GPx5, GPx7 and GPx8. It shows a high similarity amongst all the GPx.
JH594663.1
This contig is located in reverse chain and has three exons and two introns, with a total length of 626 nucleotides (15087562-15086936). The Sec is located in the first exon. The predicted SECIS element with grade A is located 368 nucleotides from the last exon and 955 nucleotides from the Sec.
The Sec of Trichechus manatus latirostris is aligned with the Sec of Loxodonta africana GPx1, GPx2, GPx3, GPx4 and GPx6 and with the homologous cysteine of GPx5, GPx7 and GPx8. It shows a high similarity amongst all the GPx.
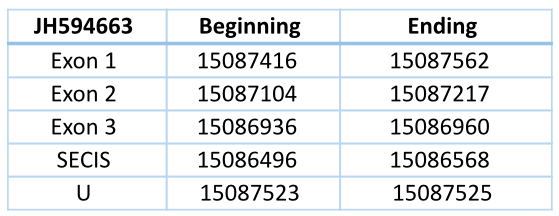
JH594786 Reverse
In Blast file we saw that this contig had different frames, so we had to separate the contig in forward frame and reverse frame (we did the process with forward frame and then with reverse frame). They are exons in different strands so they are different genes.
In Trichechus manatus latirostris the contig JH594786 in the reverse chain is codified by five exons and four introns. It has a length of 7663 nucleotides.
The contig shows a high similarity to all the GPx of Loxodonta africana, but the selenocysteine of Trichechus manatus (located in the second exon) is aligned with the Sec of Loxodonta africana GPx1, GPx2, GPx3, GPx4 and GPx6 and with the homologous cysteine of GPx5, GPx7 and GPx8.
The SECIS element (predicted with a grade A) is located 554 nucleotides of the last exon and 5492 nucleotides of the selenocysteine.
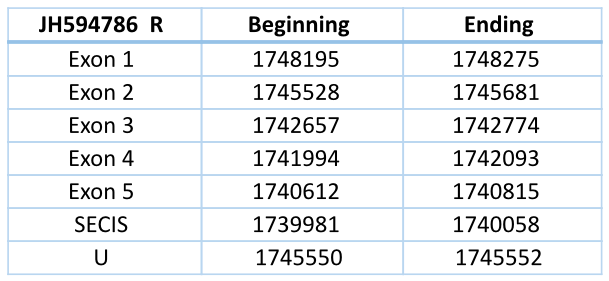
JH594786 Forward
This contig contains several Sec residues, but when we align all the GPx of Loxodonta africana we see one in particular aligned with a Sec residue of GPx1, GPx2, GPx3, GPx4, GPx6 and Cys residue of the rest of GPx of Loxodonta africana.
This contig is located in the forward chain and has a length of 49733 nucleotides. It has four exons and three introns. The Sec residue that aligns with the GPx of Loxodonta africana is located in the third exon. Any SECIS element could be predicted for this structure.
Thioredoxin Reductases (Trx) Family
The redox system of the cell is constituted by the thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) the thioredoxin (Trx) and the NADPH. The above enzymes are highly homologous with glutathione reductase, although its catalytic mechanism is distinct. These proteins are quite multifaceted because they can perform different functions: they can act both controlling the redox function of thioredoxin molecule and working as a reducer of different substrates [3] [25].
The main substrate of TrxR is the Trx, which have thiosulfate reducing capacity. Its role is essential because it reduces the ribonucleotide reductase, which is an enzyme required for DNA synthesis [3] [25].
Mammals have three TrxR selenoproteins: cytosolic TrxR1, mitochondrial TrxR2 and testicle TrxR3 / thioredoxin glutathione reductase (TGR) [16].
Given that alternative splicing occurs there may be a variety of isoforms of this enzyme [3] [25]. Thioredoxin glutathione reductase (TGR) evolved prior to the split of tetrapods through a duplication of an ancestral TR1 protein containing a glutaredoxin domain. Overall, the data suggests that mammalian TR1 and TGR evolved by gene duplication from the ancestral protein that is similar to fish TR1, and this happened prior to the appearance of amphibians. Some time after the duplication, the Grx domain was retained in TR1 only in an alternative isoform, which was lost in rodents [16].
We found three different contigs within the TR family. We cannot differ which one is TR1, TR2 or TR3, because we found the same pool of contigs in every analysed query against Loxodonta africana. So there are three different contigs:
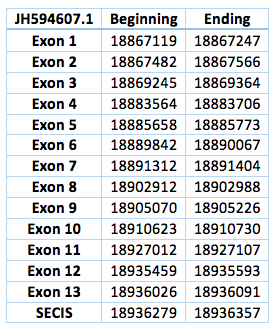
The TR protein is found in contig JH594607.1, in contig JH594633.1 and also in contig JH594888.1. We analysed each contig separately. The first one is located in scaffold JH594607.1 The protein has 13 exon, the length in the genome is 68972 bp, it has a forward frame and it is located from the position 18867119 until 18936091 of the scaffold. A single Selenocistein is located in the 13 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelI protein found in SelenoDB. We found a grade A SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 18936279 to 18936357 of the scaffold.
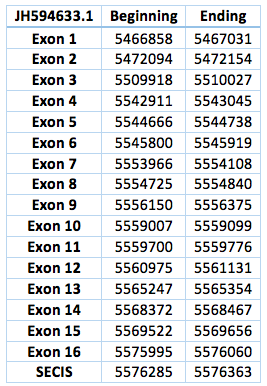
The second one is located in scaffoldJH594633.1. The protein has 16 exon and 15 introns. The length in the genome is 109202 bp, it has a forward frame and it is located from the position 5466858 until 5576363 of the scaffold. A single Selenocistein is located in the 16 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelI protein found in SelenoDB. We found a grade A SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 5576285 to 5576363 of the scaffold.
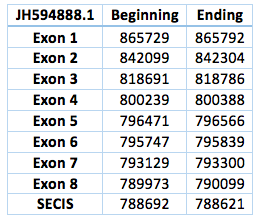
The third one is located in scaffold JH594888.1. The protein has 8 exon and 7 introns. The length in the genome is 75630 bp, it has a reverse frame and it is located from the position 865729 until 790099 of the scaffold. A single Selenocistein is located in the 8 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelI protein found in SelenoDB. We found a grade A SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 788692 to 788621 of the scaffold. Although we were not able to find a properly Sec-Sec alingment in T-Coffee, in fact we could find it in Exonerate file.
Iodotyrosine Deiodinase (DI) Family
The iodothyronine deiodinases (DI) regulate activation and inactivation of thyroid hormones. There are three DI enzymes known in mammals, all of which contain Sec: DI1, DI2, DI3. The deiodinases possess a thioredoxin-fold and show significant intrafamily homology.
DI1
The DI1 is mostly expressed in the liver, kidney, thyroid and the pituitary gland. This protein catalyzes the deiodination of T4 prohormone to its active form (T3) and regulates the circulation of the thyroid gland [3] [25].
DI2
The DI2 is also expressed in the thyroid and pituitary gland. In addition, it can also be found the CNS, in skeletal muscle and brown adipose tissue. Performs the same function as the DI1 [3] [25].
DI3
The DI3 basically expressed in fetal tissues and in the uterus of the mother. Unlike previous, this protein converts T4 to reverse T3, which is an inactive form [3] [25].
We found three different contigs within the DI family. We cannot differ which one is DI1, DI2 or DI3, because we found the same pool of contigs in every analysed query against Loxodonta africana. So there are three different contigs:
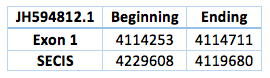
The DI protein is found in contig JH594812.1, in contig JH594621.1 and also in contig JH594651.1. We analysed each contig separately. The first one is located in scaffold JH594812.1. The protein has 1 exon, the length in the genome is 458 bp, it has a forward frame and it is located from the position 4114253 until 4114711 of the scaffold. A single Selenocistein is located in the 1 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant DI protein found in SelenoDB. We found a grade A SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 4229608 to 4119680 of the scaffold.
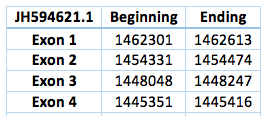
The second one is located in scaffold JH594621.1. The protein has 4 exons and 3 introns. The length in the genome is 2831 bp, it has a reverse frame and it is located from the position 1462301 until 1445416 of the scaffold. Selenocistein is located in the second exon. Although two SECIS were predicted no one was in the 3' UTR region. This way we could not predict any SECIS.
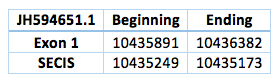
The third one is located in scaffold JH594651.1. The protein has 1 exon. The length in the genome is 491 bp, it has a reverse frame and it is located from the position 10435891 to 10435173 of the scaffold. Selenocistein is located in the 1 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelI protein found in SelenoDB. We found a grade A SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 10435249 to 10435173 of the scaffold.
The methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA) is a cysteine homologous whose function is to repair the oxidative damage of the proteins through the reduction of methionine sulfoxide to methionine [38].
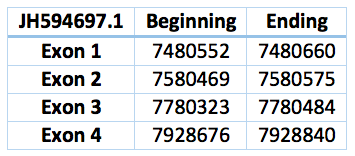
We found a match in contig JH594697.1, but we could not find an homologous selenoprotein in the genome of Trichechus manatus latirostris. The protein has 4 exons and 3 introns. The length in the genome is 539 bp, it has a forward frame and it is located from the position 7480552 until 7928840 of the scaffold. We could not find a SECIS element in the SECISearch3.
Selenoprotein 15 is expressed in a high diversity of tissues. Its expression is higher in lungs, brain, thyroid gland, kidneys and testicles. Since they are located in the endoplasmic reticulum it is though to be involved in redox functions and to participate in the correct folding of proteins. However, its function is not fully clear [3].
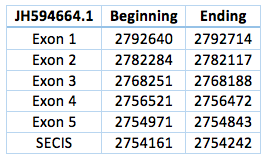
We found an homologous selenoprotein in the genome of Trichechus manatus latirostris, in the scaffold JH594664.1. The protein has 5 exons and 4 introns, the length in the genome is 37.871 bp, it has a revers frame and is located from the position 2.754.843 until 2.792.714 of the scaffold. Selenocysteine is located on the 3rd exon. We also were able to predict a SECIS in the position 2.754.242 to 2.754161, with a difference of 729 bp to the last exon of the protein and 13.929 bp to the Sec.
The Selenoprotein H is widely expressed in different tissues. It has a fold similar to thioredoxin. This indicates that it may have a similar function. It has been suggested that SelH participate in the regulation of gene expression in the synthesis of glutathione and that it also plays a role in the response to the redox reactions [29].
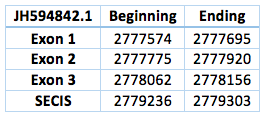
We found an homologous selenoprotein in the genome of Trichechus manatus latirostris, located in contig JH594842.1. The protein has 3 exons and 2 introns. The length in the genome is 582 bp, it has a forward frame and it is located from the position 2777574 until 2778156 of the scaffold. Selenocistein is located in the 2 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelH protein found in SelenoDB.
We found an homologous selenoprotein in the genome of Trichechus manatus latirostris, located in contig JH594842.1. The protein has 3 exons and 2 introns. The length in the genome is 582 bp, it has a forward frame and it is located from the position 2777574 until 2778156 of the scaffold. Selenocistein is located in the 2 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelH protein found in SelenoDB.
Selenoprotein I contains a highly conserved CDP-alcohol phosphatidyltransferase domain. This transmembrane protein include an homologous sequence to the enzymes responsible for phospholipids synthesis and it's expressed in all tissues that required the biosynthesis of this lipids [29].
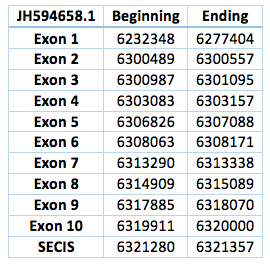
We found an homologous selenoprotein in the genome of Trichechus manatus latirostris, located in contig JH594658.1.The protein has 10 exons and 9 introns. The length in the genome is 87652 bp, it has a forward frame and it is located from the position 6232348 until 6320000 of the scaffold. A single Selenocistein is located in the 10 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelI protein found in SelenoDB.
We found a grade A SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 6321280 to 6321357 of the scaffold.
The selenoprotein K decrease the levels of intracellular ROS. It acts as an antioxidant especially protecting cardiomyocytes from oxidative stress [3].
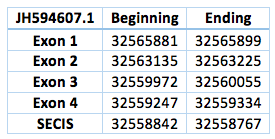
We found an homologous selenoprotein in the genome of Trichechus manatus latirostris, located in contig JH594607.1. The protein has 4 exons and 3 introns. The length in the genome is 6547 bp, it has a reverse frame and it is located from the position 32565881 until 32559334 of the scaffold. A single Selenocistein is located in the 4 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelI protein found in SelenoDB.
We found a grade A SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 32558842 to 32558767 of the scaffold.
The Selenoprotein M is involved in redox reactions. It has an important role in protecting against oxidative damage in the brain and may potentially function in calcium regulation [3] [27].
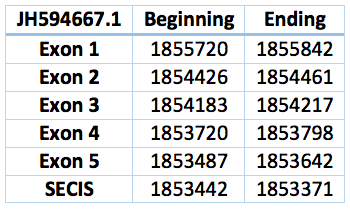
We found an homologous selenoprotein in the genome of Trichechus manatus latirostris, located in contig JH594667.1. The protein has 5 exons and 4 introns. The length in the genome is 2078 bp, it has a reverse frame and it is located from the position 1855720 until 1853642 of the scaffold. Selenocistein is located in the 2 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelM protein found in SelenoDB.
We found a SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 1853442 to 1853371 of the scaffold.
The N Selenoprotein is found in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. Mutations in its gene causes myopathy [3].
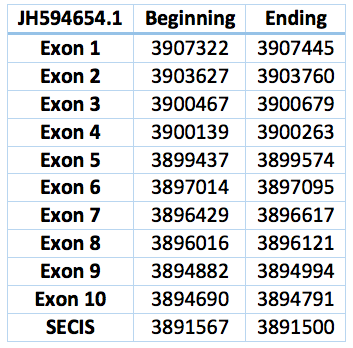
We found an homologous selenoprotein in the genome of Trichechus manatus latirostris, located in contig JH594654.1. The protein has 11 exons and 10 introns. The length in the genome is 14453 bp, it has a reverse frame and it is located from the position 3907322 until 3892869 of the scaffold. Selenocistein is located in the 8 exon. This protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelN protein found in SelenoDB.
We found a SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 3891567 to 3891500 of the scaffold.
The selenoprotein O is believed to be involved in redox reactions, however their location, distribution and exact function remain unknown [29].
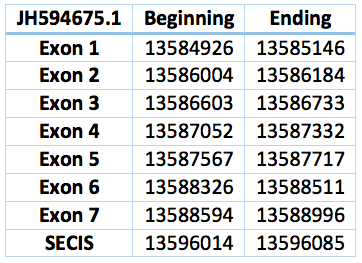
Protein SelO is located in contig JH594675.1, between positions 13584926 and 13588996. It has a forward frame. The gene contains 7 exons and 6 introns. The selenocistein is located in exon 7. The protein was predicted blasting Trichechus manatus latirostris genome against the elephant SelO protein found in SelenoDB.
We found a SECIS element of grade A predicted in the 3'UTR region. We obtained an output from SECISearch3 that matches with our results about this protein. The SECIS is in the position 3891567 to 3891500 of the scaffold.
The selenoprotein R or methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase protects proteins from oxidative damage mediated by oxidized methionine residues obtained in response to the increase in ROS elements [3].
An homologous selenoprotein was founded in the Trichechus manatus latirostris. We can suspect that is a SelR1 protein because this contig was found only with the Blast search against SelR1 elephant protein. It is located in the JH594630.1, with a revers frame and between the positions 1.575.369 and 1.578.750. The length is 3381 bp and includes 4 exons and 3 introns.
A SECIS sequence is predicted between the positions 1.574.836 and 1.574.907. The distance to the Sec is 1651 and to the last exon of the protein 462.

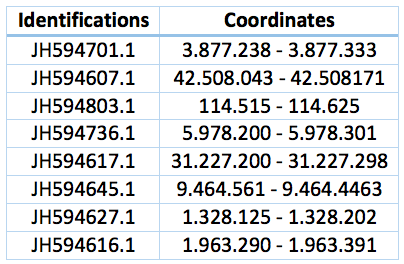
Curiously we also found 8 fragments of this protein that includes the selenocysteine through all the Trichechus manatus latirostris genome. Coordinates and identifications are in the table bellow. This could be a repetition in the genome or a computational error.
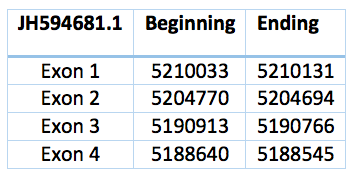
We have two more proteins that could be either SelR2 or SelR3. A phylogenetic tree is necessary to differentiate it. They have not any selenocystein. One is located in the scaffold JH594681.1, has 3 introns and 4 exons and coordinates are 5.190.913 - 5.210.033. The length is 19.120 bp and the frame revers.
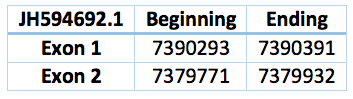
The other one is 10361 bp long, coordinates are 7.379.932 - 7.390.293 with revers frame and the scaffold JH594692.1. This second one was predicted with a human protein, for this reason we can see more differences in the alignment.
We have seen that the expression of the selenoprotein S is induced as a response to the endoplasmic reticulum stress and conversely, is inhibited when glucose is present. Moreover, it was observed that interacts with serum amyloid A (acute phase inflammatory protein). It has been suggested their involvement in various diseases such as type II diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease, as well as a role in controlling the inflammatory response [3].
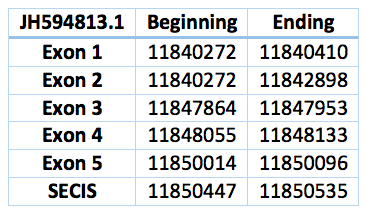
It seems that we found an homologous to this selenoprotein in the Trichechus manatus latirostris genome. We were not able to obtain a perfect alignment because it differes from one nucleotid, however we interpret it as an U-U alignment. It is located in the scaffold JH594813.1 and the lenght is 9824 bp. It has 5 exons and 4 introns. Coordinates are .11840272 - 11850535 and Sec is located 60096 in the last exon.
We found a SECIS element, predicted in the 3’UTR region. The SECIS is in the position 11850447 to 11850535 of the scaffold.
The selenoprotein T is located in the endingoplasmic reticulum and has a sequence and folding similar to the thioredoxin. Because it is believed to be related to the phenomena of cellular stress and the activation of adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide in the pituitary by regulating calcium [29].
This selenoprotein was predicted in the Trichechus manatus latirostris genome. We found two contigs but we selected the one with the best alignment compared with Loxodonta africana SelT protein. It is located in the scaffold JH594668.1 and has a length of 24.257 bp, 5 exons and 4 introns and a revers frame. Is located in between the positions 9.304.295 – 9.328.809. The Sec is in the position 9.191.574, in the second exon. The SECIS predicted is located 571 bp far from the last exon and 4702 bp from the Sec.

The function of this familly remain unkonwn. It belongs to the tioredoxin superfamilly. SelU1 is expressed in the bone tissue, brain, liver and kidneys [33] [34].
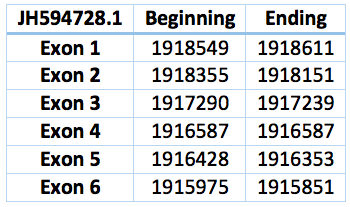
We predicted three proteins with forward frames, neither of them have any selenocystein as well as the Loxodonta africana protein. In the scaffold JH594691.1 there is a protein with only one exon. It has 669 bp long and the coordinates are 6.576.042 - 6.575.370. We also found a bigger protein in the scaffold JH594728.1 with 2.574 bp long and in the position 1.915.975 - 1.918.549. 6 exons and 5 exons were predicted by exonerate. Both could be SelU1 or SelU3.

Another one is located in the scaffold JH594641.1, has also one exon, coordinates are 14.164.022 - 14.164.596 and the length is 574 bp. This prediction only appears doing blast with SelU2 Loxodonta africana protein. Therefore we can suspect that is a SelU2 Trichechus manatus latirostris protein.

The selenoprotein V expression is limited to the testis. Its sequence and folding is very similar to the thioredoxin, consequently, although its role is not clear, is believed to be involved in redox functions [29]. SelV was the least conserved mammalian selenoprotein that likely arose from a duplication of SelW in the placental stem. SelW and SelV exhibited the same gene Structure. Each contained 6 exons. Exon 6 contained only the last portion of the 3′-UTR, including the SECIS element [16].
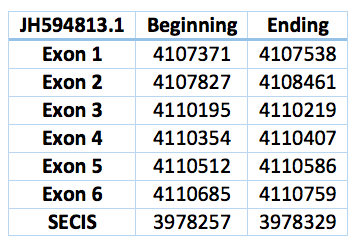
We found a lot of hits aligned with this regions. Finally we choose the only one where the Sec was aligned with a TGA codon in exonerate. This homologous selenoprotein is located in the scaffold JH594813.1, has 6 exons, 5 introns and is in the positions 4.107.371 - 4.110759 with 3388 bp. The Sec is in the position 4.110.207, in the third exon. The SECIS predicted is located 10984 bp far from the last exon and 11536 bp from the Sec. It is between the positions 3.978.329 and 3.978.257.
The selenoprotein W is highly conserved in mammals and is expressed in a variety of organs. It is steadily expressed in the brain, but in other tissues it depends on the amount of selenium. Mainly, is located in the cytoplasm, but a small fraction could also be found linked to the cell membrane. It is seen that Sel W binds glutathione with high affinity and therefore is believed to be involved in the protection of oxidative stress, performing antioxidant functions. Likewise it has been observed that this selenoprotein is located in the muscle suggesting that plays an important role in muscle and their metabolism and consequently is believed to be involved in several muscle diseases [3] [25] [30].
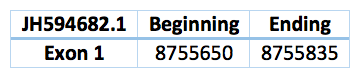
In the Trichechus manatus latirostris genome we predicted a selenoprotein. Is located in the scaffold JH594682.1 and the position 8.755.650 - 8.755.835. The length is 185 with only one exon and a revers frame. The Sec's alinement corresponds with the SelW1 Loxodonta africana protein, so we can suspect that coud be the SelW1 Trichechus manatus latirostris protein, but we cannot conclude it. However, any SECIS was predicted.
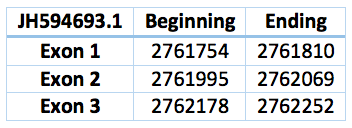
Another contig predicted is in the scaffold JH594693.1 and the position 2.761.754 - 2.762.252. It has 3 exons and 2 introns. The length is 498 bp.
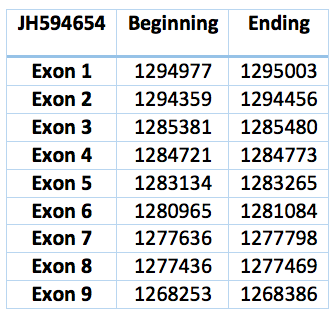
SECp43 is a RNA-binding protein that associates specifically with mammalian selenocysteine tRNA (tRNA(Sec)) [31] [37].
This protein can be find in Trichechus manatus latirostris contig JH594654.1. It is 26750 nucleotides long (1268253-1295003) and has nine exons and eight introns. Its aminoacid sequence is exactly identical to SECp43 of Loxodonta africana .
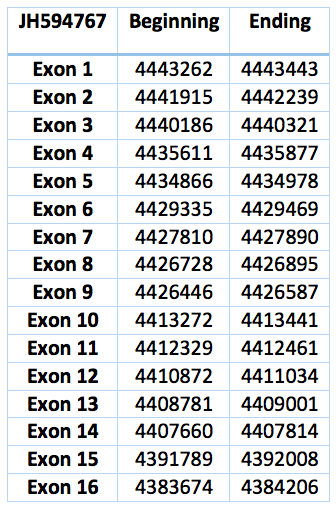
SECIS-binding protein 2 (SBP2)
This gene encodes a nuclear protein that functions as a SECIS binding protein. The complex ribosomal SBP2-SECIS led by UGA sequence recognizes the group formed by SectRNA [Ser] Sec and provides a selenocisteine to the protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a reduction in activity of a specific thyroxine deiodinase, a selenocysteine-containing enzyme, and abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants [35].
The protein predicted in Trichechus manatus latirostris is the contig JH594767.1. It has sixteen exons and fifteen introns. It is 59769 nucleotides long (4383674-4443443) and is almost identical to the one in Loxodonta africana except for isolated residues.
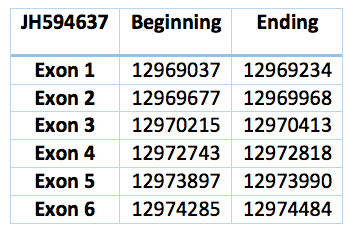
Phosphoseryl-tRNA kinase (PSTK)
PSTK specifically phosphorylated the seryl moiety on seryl-tRNA[Ser]Sec and, in addition, had a requirement for ATP and Mg2+. PSTK has been highly conserved in evolution suggests that it plays an important role in selenoprotein biosynthesis and/or regulation [36].
The sequence is 5447 nucleotides long (12969037-12974484) and is composed of six exons and five introns in the contig JH594637.1 and in the forward frame. While analysing this contig in T-Coffee we realised that this contig codifies for a protein practically identical to PSTK of Loxodonta africana .
Eukaryotic elongation factor, selenocysteine-tRNA-specific (eEFSec)
SECIS binding induces a conformational change in SBP2 that recruits eEFSec, which in concert with the Sec incorporation domain gains access to the ribosomal A site. Sec codon specificity is driven primarily by eEFSec [32].
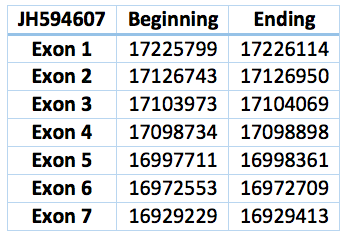
The corresponding contig in Trichechus manatus latirostris is JH594607.1. It is 296885 nucleotides long (16929229-17226114), contains seven exons and six introns. Except for ten residues, the rest of the aminoacid sequence is identical to eEFSec of Loxodonta africana .
Selenophosphate Synthetase (SPS)
SPS1
We selected one of three possible contigs because it showed the best alignment with Loxodonta africana SPS1 protein. The contig is JH594673.1 and has eight exons and seven introns. It has a length of 21321 nucleotides. The T-coffee alignment shows perfectly symmetry with Loxodonta africana SPS1.

SPS2
The function of selenophosphate synthetase 2 (SPS2) is to generate the Se donor compound (selenophosphate), which is necessary for Sec biosynthesis, and interestingly it is itself a selenoprotein. Although SPS2 was found as a selenoprotein in all vertebrates, we observed that a gene replacement took place. SPS2b arose by reverse transcription (retrotransposition) following the monotreme/marsupial split and eventually replaced SPS2a in placental mammals. [16].
The contig is JH594776.1 and has one unique exon with a total length of 1343 nucleotides. The T-coffee alignment shows that this contig nearly matches perfectly with Loxodonta africana SPS2.

Is a selenocysteinyl-tRNA synthase that catalyzes the final step of selenocysteine formation by a tRNA-dependent mechanism. Specifically, this enzime converts O-phosphoseryl-tRNASec (Sep-tRNASec) to selenocysteinyl-tRNASec (Sec-tRNASec) using a selenium donor.
It has been compared with Homo sapiens genome, since Loxodonta africana does not cointain this protein. It corresponds to the contig of Trichechus manatus latirostris JH594640 and has eleven exons and ten introns, with a length of 32504 nucleotides.